Map of the Amazon Rainforest
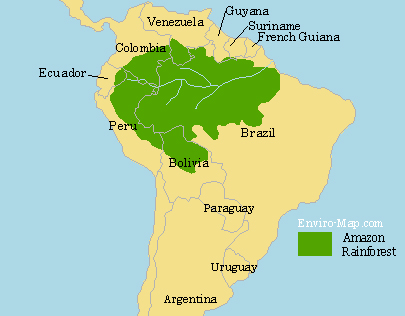
The Extent of the Rainforest
The Amazon Rainforest is about 5.5 Million square kilometers and it represents over half of the planets remaining rainforests. It is estimated that about 587,000 square kilometers of the Amazon has been deforested since the colonization by the Europeans. The deforested land is primarily used for raising cattle and farming soybeans. The map above shows the current extent of the Amazon.
The Importance of the Amazon Rainforest
The Amazon represents over half of the world’s rainforest and it is the most species rich biome in the world. It is estimated that one third of all species live in the Amazon. There are still many more plant and animal species not yet discovered. Many of these species could contain substances valuable for producing various types of medicine.
The plants in the Amazon absorb and contain carbon from the air. Therefore destruction of the rainforest would release carbon into the atmosphere, accelerating global warming. Burning of the rainforest has made Brazil one of the top greenhouse gas producers in the world.
Deforestation
From 1990 to 2003 the annual rate of deforestation had increased due to local, national and international factors. 70 percent of all the deforested land is used for raising livestock such as cattle. The remainder is primarily used for growing soybeans and sugarcane, making Brazil the second largest producer of soybeans in the world.
Another contributing factor to deforestation is the growing interest in biofuel. As the world’s fossil fuel resources are becoming more depleted, the demand for biofuel is increasing. The biofuel, ethanol is produced from sugarcane in Brazil and Brazil has the largest national ethanol fuel industries in the world.

References
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amazon_Rainforest
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ethanol